The slope coefficient significance
The test of significance for the coefficient of linear regression equation
This test is used to verify the hypothesis determining the lack of a linear dependence between an analysed features and is based on the slope coefficient (also called an effect), calculated for the sample. The closer to 0 the value of 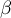 coefficient is, the weaker dependence presents the fitted line.
coefficient is, the weaker dependence presents the fitted line.
Basic assumptions:
- measurement on the interval scale,
- normality of distribution of residuals or an analysed features in a population.
Hypotheses:
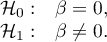
The test statistic is defined by:
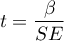
where:
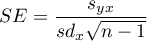 ,
,
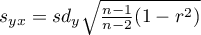 ,
,
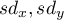 – standard deviation of the value of features:
– standard deviation of the value of features: 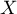 and
and 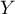 .
.
The value of the test statistic can not be calculated when 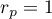 or
or 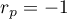 or when
or when 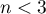 .
.
The test statistic has the t-Student distribution with 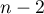 degrees of freedom.
degrees of freedom.
The p-value, designated on the basis of the test statistic, is compared with the significance level 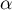 :
:
Prediction
is used to predict the value of a one variable (mainly a dependent variable 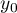 ) on the basis of a value of an another variable (mainly an independent variable
) on the basis of a value of an another variable (mainly an independent variable 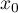 ). The accuracies of a calculated value are defined by prediction intervals calculated for it.
). The accuracies of a calculated value are defined by prediction intervals calculated for it.
- Interpolation is used to predict the value of a variable, which occurs inside the area for which the regression model was done. Interpolation is mainly a safe procedure - it is assumed only the continuity of the function of analysed variables.
- Extrapolation is used to predict the value of variable, which occurs outside the area for which the regression model was done. As opposed to interpolation, extrapolation is often risky and is performed only not far away from the area, where the regression model was created. Similarly to the interpolation, it is assumed the continuity of the function of analysed variables.
Analysis of model residuals - explanation in the Multiple Linear Regression module.
The settings window with the Pearson's linear correlation can be opened in Statistics menu→Parametric tests→linear correlation (r-Pearson) or in ''Wizard''.
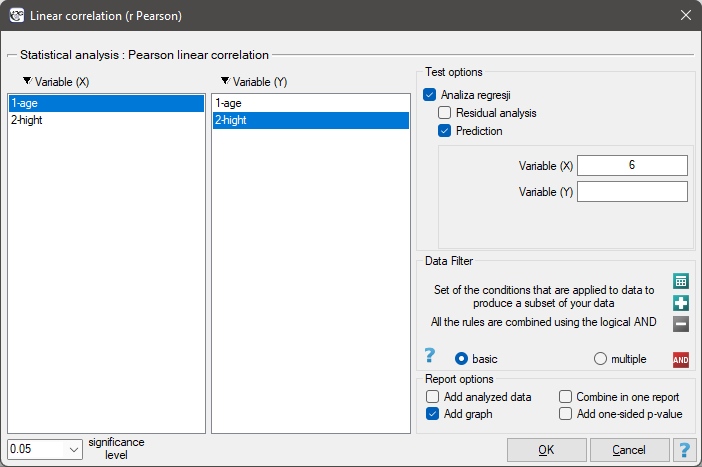
Among some students of a ballet school, the dependence between age and height was analysed. The sample consists of 16 children and the following results of these features (related to the children) were written down:
(age, height): (5, 128) (5, 129) (5, 135) (6, 132) (6, 137) (6, 140) (7, 148) (7, 150) (8, 135) (8, 142) (8, 151) (9, 138) (9, 153) (10, 159) (10, 160) (10, 162).}
Hypotheses:
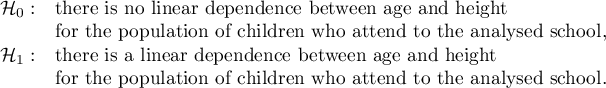
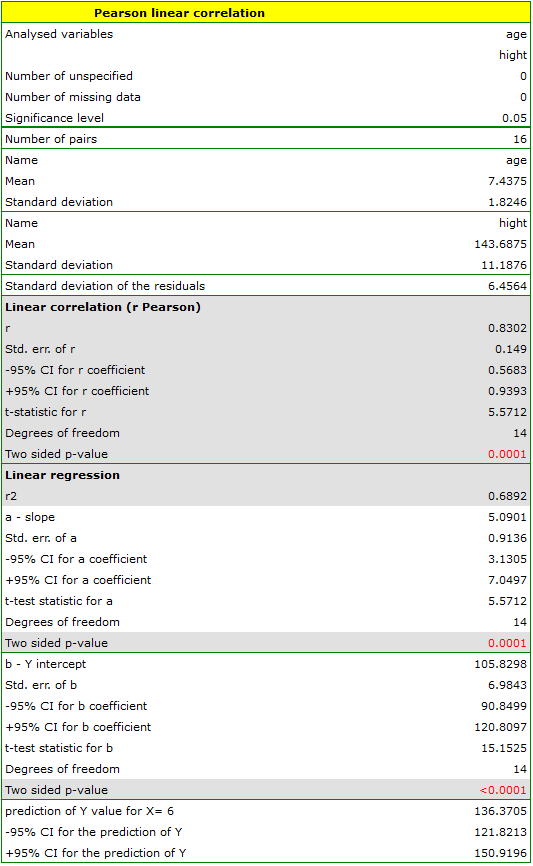
Comparing the 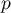 value < 0.0001 with the significance level
value < 0.0001 with the significance level 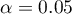 , we draw the conclusion, that there is a linear dependence between age and height in the population of children attening to the analysed school. This dependence is directly proportional, it means that the children grow up as they are getting older.
, we draw the conclusion, that there is a linear dependence between age and height in the population of children attening to the analysed school. This dependence is directly proportional, it means that the children grow up as they are getting older.
The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, so the strength of the linear relation between age and height counts to 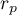 =0.83. Coefficient of determination
=0.83. Coefficient of determination 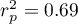 means that about 69\% variability of height is explained by the changing of age.
means that about 69\% variability of height is explained by the changing of age.
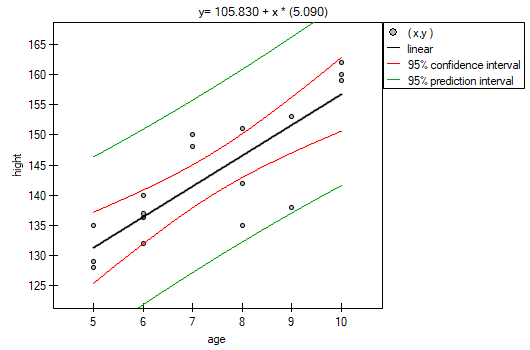
From the regression equation:
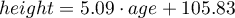 it is possible to calculate the predicted value for a child, for example: in the age of 6. The predicted height of such child is 136.37cm.
it is possible to calculate the predicted value for a child, for example: in the age of 6. The predicted height of such child is 136.37cm.