The Kendall's tau correlation coefficient
The test of significance for the Kendall's 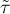 correlation coefficient is used to verify the hypothesis determining the lack of monotonic correlation between analysed features of population. It is based on the Kendall's tau correlation coefficient calculated for the sample. The closer to 0 the value of tau is, the weaker dependence joins the analysed features.
correlation coefficient is used to verify the hypothesis determining the lack of monotonic correlation between analysed features of population. It is based on the Kendall's tau correlation coefficient calculated for the sample. The closer to 0 the value of tau is, the weaker dependence joins the analysed features.
Basic assumptions:
- measurement on an ordinal scale or on an interval scale.
Hypotheses:
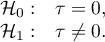
The test statistic is defined by:
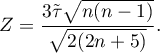
The test statistic asymptotically (for a large sample size) has the normal distribution.
The p-value, designated on the basis of the test statistic, is compared with the significance level 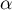 :
:
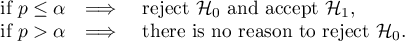
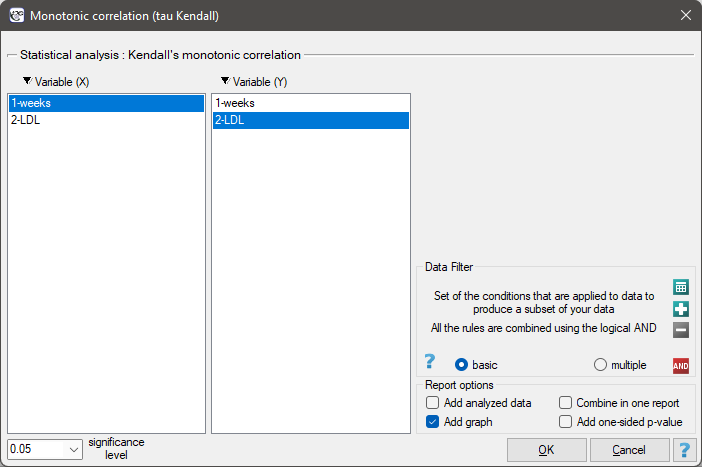
The settings window with the Kendall's monotonic correlation can be opened in Statistics menu → NonParametric tests→monotonic correlation (tau-Kendall) or in ''Wizard''.
EXAMPLE cont. (LDL weeks.pqs file)
Hypotheses:
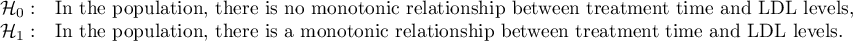
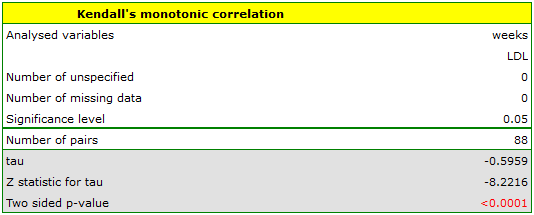
Comparing p<0.0001 with a significance level 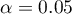 we find that there is a statistically significant monotonic relationship between treatment time and LDL levels. This relationship is initially decreasing and begins to stabilize after 150 weeks. The Kendall's monotonic correlation coefficient, and therefore the strength of the monotonic relationship for this relationship is quite high at
we find that there is a statistically significant monotonic relationship between treatment time and LDL levels. This relationship is initially decreasing and begins to stabilize after 150 weeks. The Kendall's monotonic correlation coefficient, and therefore the strength of the monotonic relationship for this relationship is quite high at 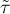 =-0.60. The graph was plotted by curve fitting through local LOWESS linear smoothing techniques.
=-0.60. The graph was plotted by curve fitting through local LOWESS linear smoothing techniques.
