Basic definitions
Geographic Information System - GIS – is a system for entering, storing, processing, and visualization of geographic data. From the technical point of view GIS is a tool which allows the analysis of interrelated:
- information about spatial locations of objects – represented by means of a map;
- descriptive characteristic concerning objects presented on a map – represented by means of a database.
Objects represented by means of a map are:
- Points – the location of which, in 2D, is defined with the help of two coordinates
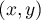 ;
; - Multipoints – they are points grouped in sets:
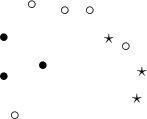 An example of a multipoint in which each point is defined as belonging to one of 3 groups.
An example of a multipoint in which each point is defined as belonging to one of 3 groups.
- Lines – they are created by linking subsequent points, in proper order (lines can intersect);
- Polygons – they are closed spaces, restricted by means of external rings (closed lines which do not intersect and which go through at least 3 points, in an appropriate order). Polygons can also contain internal rings constituting their internal boundaries. External rings are defined clockwise and the internal ones the other way round.
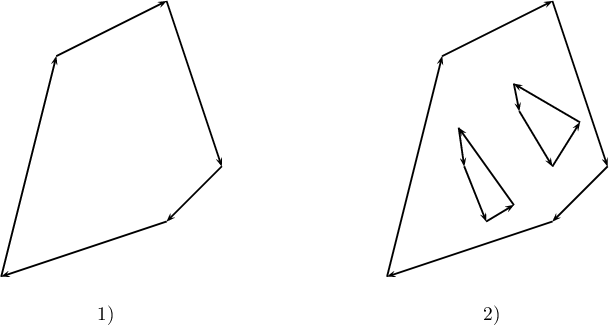
- 1) An example of a polygon which only has an external boundary (with no internal rings);
- 2) An example of a polygon which has both an external boundary and internal boundaries (areas defined by the internal rings constitute a part of an external area, i.e. they do not belong to the polygon).
Object attributes are entered into the base in the form of:
numbers – e.g. area, temperature,
texts – e.g. names of objects.
Map projection is a mathematical method of mapping the surface of the Earth onto a map surface. There is a number of methods for such mapping. The mappings can be based on a spheroid or on the surface of a ball (a sphere), or on a part of either of them. Each mapping forms the basis for defining an appropriate coordinate system. Because each projection of a surface entails certain distortions (distortions of angles, areas, lengths), the choice of a proper system depends on the aim for which the map is to be used.
Coordinate systems used in cartography are classified as:
- geographic coordinate systems (they define geographic latitude and longitude);
- cartesian coordinate systems;
- polar coordinate systems.
For a map to be loaded correctly, the program PQStat requires a vector map saved in a SHAPEFILE (shp) type of file and defined in a proper Cartesian coordinate system, with line scale.
The program tries to automatically detect maps with geographic coordinates. If, while importing the map, the program detects a geographic coordinate system, it suggests converting the coordinates into a UTM system (Universal Transverse Mercator), on the basis of the WGS-84 system of reference. As conversion might be incorrect (due to the use of many geographic coordinate system and the lack of certainty with regard to the applied system), it is recommended that properly prepared maps be used – in a Cartesian coordinate system.