Interctions
Interactions are considered in multidimensional models. Their presence means that the influence of the independent variable (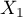 ) on the dependent variable (
) on the dependent variable (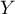 ) differs depending on the level of another independent variable (
) differs depending on the level of another independent variable (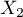 ) or a series of other independent variables. To discuss the interactions in multidimensional models one must determine the variables informing about possible interactions, i.e the product of appropriate variables. For that purpose we select the
) or a series of other independent variables. To discuss the interactions in multidimensional models one must determine the variables informing about possible interactions, i.e the product of appropriate variables. For that purpose we select the Interactions button in the window of the selected multidimensional analysis. In the window of interactions settings, with the CTRL button pressed, we determine the variables which are to form interactions and transfer the variables into the neighboring list with the use of an arrow. By pressing the OK button we will obtain appropriate columns in the datasheet.
In the analysis of the interaction the choice of appropriate coding of dichotomous variables allows the avoidance of the over-parametrization related to interactions. Over-parametrization causes the effects of the lower order for dichotomous variables to be redundant with respect to the confounding interactions of the higher order. As a result, the inclusion of the interactions of the higher order in the model annuls the effect of the interactions of the lower orders, not allowing an appropriate evaluation of the latter. In order to avoid the over-parametrization in a model in which there are interactions of dichotomous variables it is recommended to choose the option effect coding.
In models with interactions, remember to „trim” them appropriately, so that when removing the main effects, we also remove the effects of higher orders that depend on them. That is: if in a model we have the following variables (main effects): 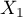 ,
, 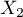 ,
, 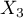 and interactions:
and interactions:  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 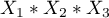 , then by removing the variable
, then by removing the variable 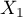 from the model we must also remove the interactions in which it occurs, viz:
from the model we must also remove the interactions in which it occurs, viz:  ,
,  and
and 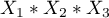 .
.